Key Takeaways:
· Understanding the concept of vulnerability management is key to securing your assets.
· Wherever necessary, proper implementation of a structured process will avoid many of the risks and breaches.
· Collaboration coupled with continuous improvement stands between cybersecurity threats and good defenses.
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction to Vulnerability Management
2. Why Vulnerability Management Matters
3. Key Steps in Vulnerability Management
4. Tools and Technologies
5. Best Practices
6. Continuous Improvement
7. Conclusion
Introduction to Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is a proactive security approach whereby security vulnerabilities in an organization’s assets are identified, detected, classified, and remedied. It requires an ongoing process that involves the identification, description, and mitigation of the vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by an attacker to compromise an asset. Such processes need to help organizations reduce the overall risk for cyber-attacks and data breaches by prioritizing possible threats and taking appropriate action against them regarding vulnerability management. Besides that, knowing the basics will protect your assets and ensure business continuity. The proactive approach protects sensitive data and also secures information that creates confidence in clients and stakeholders in general.
Why Vulnerability Management Matters
Cyber threats have been developing very fast in this current digital era. The threats can range from simple malware to major state-sponsored cyber-attacks. The potential sound of this figure gives a clear indication of the urgency organizations need to adopt serious security measures in place, including good vulnerability management.
Proper management finds the weak spots before they become problems, hence reducing the overall possibility of expensive damages. Having a vulnerability management program puts one always one step ahead of the cybercriminals, insuring needed measures for sensitive data protection and business continuity. So, with today’s increasingly connected systems, the stakes have never been higher for businesses to be vigilant and proactive.
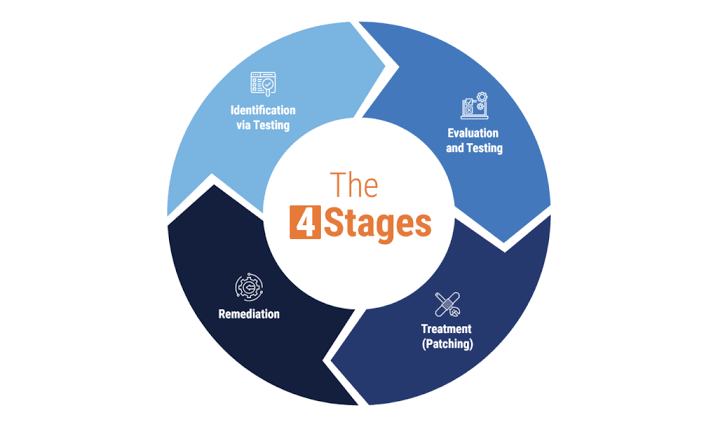
Key Steps in Vulnerability Management
Well, asset discovery really involves the identification of all the assets within your network: hardware, software, and information. This forms the first step so that one may know who and what to protect. Eventually, a proper asset inventory lays the foundational success in vulnerability management.
Vulnerability Assessment: Scanning of your systems for any kind of vulnerabilities is done regularly. Moreover, such automated scanning ensures that no stone is left unturned. What’s more, periodic assessments need to be conducted so that one can stay well ahead of potential dangers.
Risk Assessment: Assess the risks identified with these vulnerabilities, then prioritize according to potential impact. Certainly, all vulnerabilities are not created equal; some could pose greater immediate risks than others. Prioritization allows for efficient resource allocation.
Remediation: Apply patches or fixes to patch critical vulnerabilities as soon as possible; this may include deploying a patch, a system configuration, or any required step to nullify the threat. Quick and efficient remediation can help avoid the operation of vulnerability exploitation.
Verification: Confirm that the applied fixes are effective and the vulnerability is resolved. Verification is all about rescanning and retesting to confirm that the vulnerabilities have, in fact been fixed. Very often, this step is ignored, while it is so critical to keep it around just for ensuring longevity of security within the system.
Tools and Technologies
IDS, SIEM systems, and patch management tools are among several tools and technologies that can be used to assist in vulnerability management. The technologies aid the identification of vulnerabilities by bringing insight to remediation. For instance, IDS detect unusual activities in an environment, which may imply a threat in advance and hence can allow timely intervention.
SIEM systems provide real-time collection and analysis of security-related data, thus presenting a consolidated view of security events. Patch management tools are indispensable in keeping systems and applications up-to-date with the latest security patches. Integration of this kind of tool offers comprehensive protection and smooths the process of managing vulnerabilities to maintain stringent security defenses.
These technologies work in harmony to offer multilayered cybersecurity that will make the attackers find it hard to breach your defenses.
Best Practices
Regular Updates: All your software and systems need to be updated regularly to protect against the latest security patches. It might be one of the easiest ways to reduce vulnerabilities, but it really works. Known vulnerabilities are patched with regular updates; the attack surface is reduced.
Employee Training: Instruct workers on the best of best practices concerning security. Let them also know why they have to follow protocols. Human error is generally viewed as the weak point in cyber security. Training regularly may equip a company’s employees with the capacity to know and avoid certain security situations:
Continuous Monitoring: Continuous monitoring should be performed to detect new vulnerabilities as fast as possible. This way you are always watching for a new threat and as soon as you catch one, you respond swiftly. Collaborate: Threat intelligence could be shared with industry partners and experts. Cybersecurity is a constantly changing field, and understanding it through cooperation with experts, in addition to peer organizations, leads to better insight and distributed resources to enhance your security posture.
Continuous Improvement
One of the very important things in this regard is the issue of creating a culture of continuous improvement that will make risk management sustainable. Regularly review and update your vulnerability management processes to ensure they remain effective. Use lessons learned from past incidents, including feedback received from third parties, to further strengthen your defenses. An organization should be adopting a security philosophy or approach which should be cyclical in nature, where continuous assessment, feedback, and correction actually provide the backbone of a sound defense strategy. Another important dimension of keeping your security posture robust is investing in Continuous Professional Development in the cybersecurity team. Perpetuating this culture of continuous improvement not only keeps your defenses up to date but also instills vigilance and a sense of responsibility in the psyches of your team members.
Conclusion
Effective management of the vulnerability will help you to keep the digital assets of your organization secure. Mitigate the risk by following a structured approach and staying committed to continuous improvement toward sustaining a strong cybersecurity posture. The threat dynamics in cybersecurity require the need for having a proactive and adaptive strategy that changes with emerging risks. More information can be found through a number of different online resources for the latest trends and best practices on cybersecurity, including CSO Online. Being well-informed and agile is important to maintaining relevant security in today’s ever-changing digital world.